If heat has to be transferred quickly through a substance, good conductors are used (metals). If heat is unwanted we use insulators to prevent themal energy from transferring quickly or minimise the loss of thermal energy.
- Uses of Good Conductors of Heat (Metals)
1) Cooking utensils
- Made of aluminium of stainless steel
- Direct heating is involved
- Requires the heat energy to cook the food
2) Soldering iron rods

- Made of iron, but tip is made of copper - copper is a much better conductor of heat
3) Heat exchangers

(Click picture to Enlarge)
The hot dirty water goes in from the tube inlet, passes the water to the cold clean water, which enters in the shell inlet and exits from the shell outlet. The hot dirty water then exits from the tube outlet.
- Uses of Bad Conductors (Insulators) of Heat (Non-Metals)
1) Handles of appliances and utensils
- Handles of cooking kettles, cooking pot, pans, irons and soldering iron rods are made of insulators of heat like wood or plastic.
- Prevents hands from getting scalded when picking it up
2) Table mats
- Usually made of cork
- Prevents table-top from getting damaged by the intensed heat from the hot kitchenware
3) Sawdust
- Used to cover ice blocks - good insulator
4) Wooden/Plastic ladles
- Good for stirring or scooping hot soups/scooping cooked rice that has just been cooked
5) Woollen clothes
- Traps heat
- Keeps people warm on cold days/winter
6) Fibreglass, felt and expanded polystyrene foam
- Traps large amounts of air
- Used as insulators in the walls of houses, ice boxes, refrigerators, etc.
- Double-glazed windows have air trapped between two panes of glass - reduces thermal energy transfer through windows
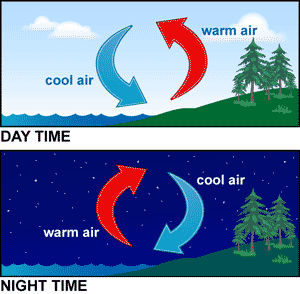
Common Applications of Convection:
1) Electric kettles
- Heating coil is always placed at the bottom of the kettle - aids transfer of thermal energy in water (convection)
- Water around the heating coil is being heated up and rises to the top as it becomes less dense
- The cooler water at the top will then sink as it is denser than the warm water
- It comes into contact with the heating coil and gets heated up, hence rising
- Hence a convection current is formed
2) Household hot water systems

3) Air conditioners
- Always installed near to the ceiling of a room to facilitate convection
- Rotary fan inside an air conditioner releases cool dry air into the room (dense, hence sinks)
- Warm air below (less dense) rises and is being cooled as it is near the air conditioner.
- Hence air is recirculated and the temperature of air will eventually fall to the desired value
4) Refrigerators
- Similiar to air conditioners
- Freezing unit is placed at the top to cool the air and facilitate convection
- Convection currents help to cool the food items inside






.jpg)