Conduction
Definition: Conduction is the process of thermal energy transfer without any flow of the material medium
This means that it is the transfer of energy through matter from particle to particle.
.jpg)
Conduction requires an object in between to transfer the thermal energy. No movement is required in conduction as the object stays in its place during conduction. The object is either called a 'good conductor of heat' or a 'poor conductor of heat', otherwise known as 'insulator', depending on the rate it conducts heat at.
Usually, metals are good conductors of heat whereas non-metals are insulators of heat.
All metals and non-metals, which are known as solids, are made up of tiny particles called atoms and molecules. The only difference is that metals have many free electrons while non-metals don't. These free electrons speed up the rate of conducting heat as they move randomly between the atoms and molecules. This will be further explained in the next paragraph.
The process of conducting heat can be illustrated with two rods, one metal and one non-metal. When you heat up the rods at one end, the particles will start vibrating more rapidly, knocking into their neighbouring particles, transferring the heat over. The neighbouring particles will start vibrating too and knock into their neighbouring particles, and it will carry the heat all the way throughout the rod. However, in metals, they have free electrons that do not seem to be attracted to any nucleus, hence are moving around very fast and by themselves. When the particles start to vibrate faster, these electrons will speed up and diffuse into the cooler parts of the metal and transfer their kinetic and heat energy to them. In this way, the electrons are helping to increase the rate of which heat spreads throughout the metal, hence metals are good conductors of heat.

Conduction in liquids and gases is of the same concept as conduction in solids. However, the particles in liquids and gases are quite far apart and hence, the chances of the particles knocking into each other is quite low. Since the particles do not really touch each other, chances of passing heat is low. Therefore, liquids and gases are poor conductors of heat as compared to solids.
The experiment below illustrates that water is a poor conductor of heat.

The water at the top nearest to the flame is boiling, but the ice cube wrapped in metal gauze at the bottom of the test tube has barely melted. This further illustrates the point that water is a poor conductor of heat.
Definition: Conduction is the process of thermal energy transfer without any flow of the material medium
This means that it is the transfer of energy through matter from particle to particle.
.jpg)
Conduction requires an object in between to transfer the thermal energy. No movement is required in conduction as the object stays in its place during conduction. The object is either called a 'good conductor of heat' or a 'poor conductor of heat', otherwise known as 'insulator', depending on the rate it conducts heat at.
Usually, metals are good conductors of heat whereas non-metals are insulators of heat.
All metals and non-metals, which are known as solids, are made up of tiny particles called atoms and molecules. The only difference is that metals have many free electrons while non-metals don't. These free electrons speed up the rate of conducting heat as they move randomly between the atoms and molecules. This will be further explained in the next paragraph.
The process of conducting heat can be illustrated with two rods, one metal and one non-metal. When you heat up the rods at one end, the particles will start vibrating more rapidly, knocking into their neighbouring particles, transferring the heat over. The neighbouring particles will start vibrating too and knock into their neighbouring particles, and it will carry the heat all the way throughout the rod. However, in metals, they have free electrons that do not seem to be attracted to any nucleus, hence are moving around very fast and by themselves. When the particles start to vibrate faster, these electrons will speed up and diffuse into the cooler parts of the metal and transfer their kinetic and heat energy to them. In this way, the electrons are helping to increase the rate of which heat spreads throughout the metal, hence metals are good conductors of heat.

Conduction in liquids and gases is of the same concept as conduction in solids. However, the particles in liquids and gases are quite far apart and hence, the chances of the particles knocking into each other is quite low. Since the particles do not really touch each other, chances of passing heat is low. Therefore, liquids and gases are poor conductors of heat as compared to solids.
The experiment below illustrates that water is a poor conductor of heat.

The water at the top nearest to the flame is boiling, but the ice cube wrapped in metal gauze at the bottom of the test tube has barely melted. This further illustrates the point that water is a poor conductor of heat.
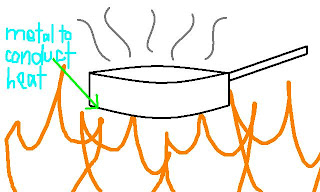
Cooking pots are made of metal and act as the medium in cooking because without the pot, the food is more likely to catch fire. Also, the pot must be a good conductor of heat as it is acting as the medium for conduction of heat. Another reason it must be a conductor of heat is because most conductors of heat are metal, and metal will not melt or burn so easily like wood or plastic at cooking temperature.
No comments:
Post a Comment